
Have you ever wondered why some products almost seem to sell themselves, while others struggle to get attention? The answer does not just lie in marketing but in the inner workings of the human brain. Neuroscience has unlocked fascinating insights into how consumers make purchasing decisions, and savvy retailers are using these findings to optimize their strategies.
This article dives into the world of shopper psychology and reveals how understanding brain science can help retailers drive engagement, increase sales, and create lasting brand loyalty.
The Science Behind Why We Buy
Did you know that 95% of purchasing decisions are made subconsciously? Thus, understanding the science behind consumer purchasing decisions is essential for businesses that are looking to enhance their marketing strategies and improve sales. The reason for consumer shopping is listed below:
- Consumer psychology dives deep into the motivations, perceptions, and behaviors of individuals that make them choose one product over another.
- Companies can tailor their approaches to meet the needs and preferences of their target audience by examining the psychological factors that influence buying behavior.
With this data retailers can craft effective marketing campaigns from the insights with consumer behavior research that will resonate with consumers on a deeper level, leading to more informed purchasing decisions. This will ultimately lead to fostering loyalty and increasing revenue.
- Emotion Over Logic
The human brain processes information in two primary ways: emotionally and logically. According to the Statista survey of US customers, emotions play a dominant role in making purchasing decisions. Depending upon the gender, different emotions that trigger the need to shop are given below:
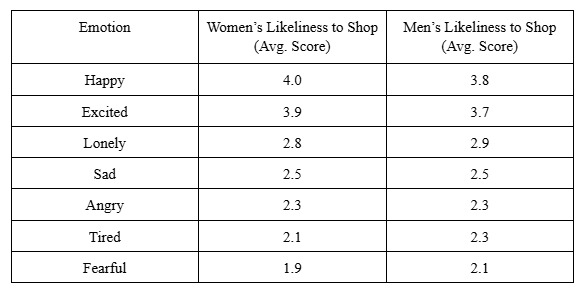
This is why people often choose brands that “feel right” over those with purely logical advantages.
Retail Application:
- Create Emotional Appeals: Retailers can use storytelling in marketing campaigns to connect with customers on an emotional level.
- Leverage Visual Cues: Using bright colors and appealing layouts triggers positive feelings which would encourage purchase behavior.
Domino’s Pizza India has transitioned from its previous campaign, “Khushiyon Ki Home Delivery,” to a new tagline, “Yeh Hai Rishton Ka Time,” to forge a stronger emotional connection with its consumers. This shift highlights the brand’s evolution over the years, as they adapt to changing consumer sentiments. Initially focusing on fulfilling hunger with the “Hungry Kya?” slogan, they later added an emotional touch with “Khushiyon Ki Home Delivery,” which emphasized the happiness associated with their pizzas. Now, with “Yeh Hai Rishton Ka Time,” Domino’s is reinventing its strategy to position itself more effectively in the Indian market, demonstrating that consumers often prioritize emotional connections over logical choices when it comes to brand loyalty.
- Dopamine Effect
When customers see a product they want, their brains release dopamine, the “feel-good” chemical. This creates a sense of anticipation and excitement, which can influence impulse buying.
Retail Application:
- Trigger Anticipation: Retailers can create urgency by using limited-time offers, countdown timers, and exclusive previews.
- Reward Loyalty: Implementation of loyalty programs by retailers that reward repeat purchases can activate dopamine pathways. This strategy changes the purchase patterns of consumers.
In 2011, Coca-Cola launched the “Share a Coke” campaign, which ran until 2014 and significantly boosted both sales and brand engagement. The campaign’s innovative approach involved replacing the iconic Coca-Cola logo on bottles with popular names, encouraging customers to find and share their personalized bottles. This strategy had a remarkable impact on Coca-Cola’s revenue, with sales figures reaching $46,542 in 2011, $48,017 in 2012, $46,854 in 2013, and $45,998 in 2014. Beyond financial success, the campaign generated an impressive 870% increase in Facebook traffic and a 7% rise in brand awareness and consumption. It highlighted the crucial role of social media in modern marketing by generating 18 million media impressions and engaging 65,000 participants in the Facebook initiative. In response to public demand, Coca-Cola also expanded the list of names available on bottles, further personalizing the product and strengthening its connection with consumers.
Dopamine Effect Utilization
- Personalization: By customizing beverages with individual names, Coca-Cola created a sense of exclusivity and distinction for each customer. This idea of personalization enhanced relevance and engagement in customer experiences, which in turn triggered a dopamine response.
- Anticipation and Reward: The thrill of discovering a bottle featured one’s name or that of a loved one fueled excitement and anticipation.
- Social Sharing: The campaign encouraged customers to share images of their personalized bottles on social media, further enhancing dopamine release through validation and approval from peers.
- Decision Fatigue
For many individuals, making decisions seems more challenging than ever. Feelings of anxiety and overwhelm can explain why choosing between two items at the grocery store can lead your customers to abandon the decision altogether and leave empty-handed. This is the Paralysis by Analysis theory of Psychology.
According to this theory, when consumers are given more choices, they tend to over-analyze every alternative to the extent that the outcome is paralyzed.
Retail Application:
- Curate Product Selections: To solve this issue, retailers can offer fewer, but carefully selected, options to their customers for better decision-making.
- Guide Choices: Retailers can also use labels like “Best Seller” or “Most Popular” which helps the customers make quicker decisions.
How Netflix Solved Paralysis Analysis:
With the sheer number of options, Netflix constantly faced the issue of Paralysis Analysis where its subscribers constantly felt overwhelmed. They found themselves spending more time deciding what to watch than enjoying the content.
Fortunately, Netflix introduced a solution to help alleviate this dilemma: the new Play Something feature. As the name suggests, Play Something was designed to recommend a show or movie based on user interests, making it easier for them to decide what to watch.
- Social Proof
Following the crowd has always been hardwired in the brain. This makes social proof a powerful influence in retail. Shoppers are more likely to purchase when they see positive reviews, testimonials, or endorsements.
Retail Application:
- Display Reviews Prominently: Retailers and F&B owners tend to highlight customer reviews and ratings on product pages.
- Showcase Popular Products: Brands use “Trending Now” or “Customer Favorites” tags to guide customer decisions.
Founded by Selena Gomez, Rare Beauty is dedicated to celebrating individuality through its range of feel-good makeup products. The brand offers a variety of vegan and cruelty-free items, including lip oils, blushes, and eyeshadows.
Rare Beauty has mastered the art of social proof marketing through several key elements. Upon visiting their website, customers are greeted by a large carousel showcasing live social media posts from users who have shared their experiences with the products. This feature instantly instills trust and credibility in the brand. Additionally, customer reviews are thoughtfully integrated into the product pages, allowing potential buyers to gauge the product’s value based on real feedback from other customers. These reviews often include photos, which enhance authenticity and alleviate any doubts shoppers may have about their purchases.
- Power of Scarcity
Loss Aversion is a phenomenon where the emotional impact of losing something is often greater than the satisfaction derived from gaining something of equal value. It is believed that when people perceive something as limited or exclusive, it becomes more desirable. Neuroscience explains this through the brain’s aversion to loss.
Retail Application:
- Highlight Limited Stock: Use phrases like “Only 3 left!” to create urgency.
- Offer Exclusive Deals: Create VIP experiences for loyal customers to make them feel special.
Amazon uses “Limited Availability” as a tool for triggering loss aversion constantly. In this, they tend to display the number of units available with them in stock prominently. For instance, they use messages like “only 3 left in stock” which acts as a strong motivator for clicking on the Add to Cart button.
Conclusion
For Retailers to understand the neuroscience behind shopping isn’t just fascinating, instead, it is transformative. By leveraging insights into how the brain processes decisions, emotions, and stimuli, retailers can create strategies that resonate deeply with customers. Whether it is about evoking emotions, reducing decision fatigue, or creating personalized experiences, neuroscience provides the blueprint for crafting compelling customer journeys.